Location Management offers support for all Geographic Information System (GIS) initiatives at Railinc and throughout the railroad industry. Location Management provides the framework that allows for the collective integration of all location data to solve problems at an industry scale. In cooperation with the Association of American Railroads (AAR) GIS Committee (GISC), Location Management improves the accuracy of existing GIS data and provides additional GIS content to Railinc’s products and services.
GIS provides for more effective decision making, adding location intelligence / spatial awareness to a wide variety of rail industry applications, including AskRail®, End of Train Self Service, Clear Path®, HBD Subscription Application, Mileage Calculations, and many more.
This page describes the following GIS-related applications:
Rail Industry GIS (RIGIS) Portal
The Rail Industry Geographic Information System Portal (RIGIS Portal) is the gateway to dynamic GIS maps and applications. It enables the railroad industry to review, update, and share GIS data associated with their assets.
RIGIS Portal users can create and share web maps and use applications. Other rail industry users can access the RIGIS Portal to visualize and analyze data.
RIGIS Portal Home Page
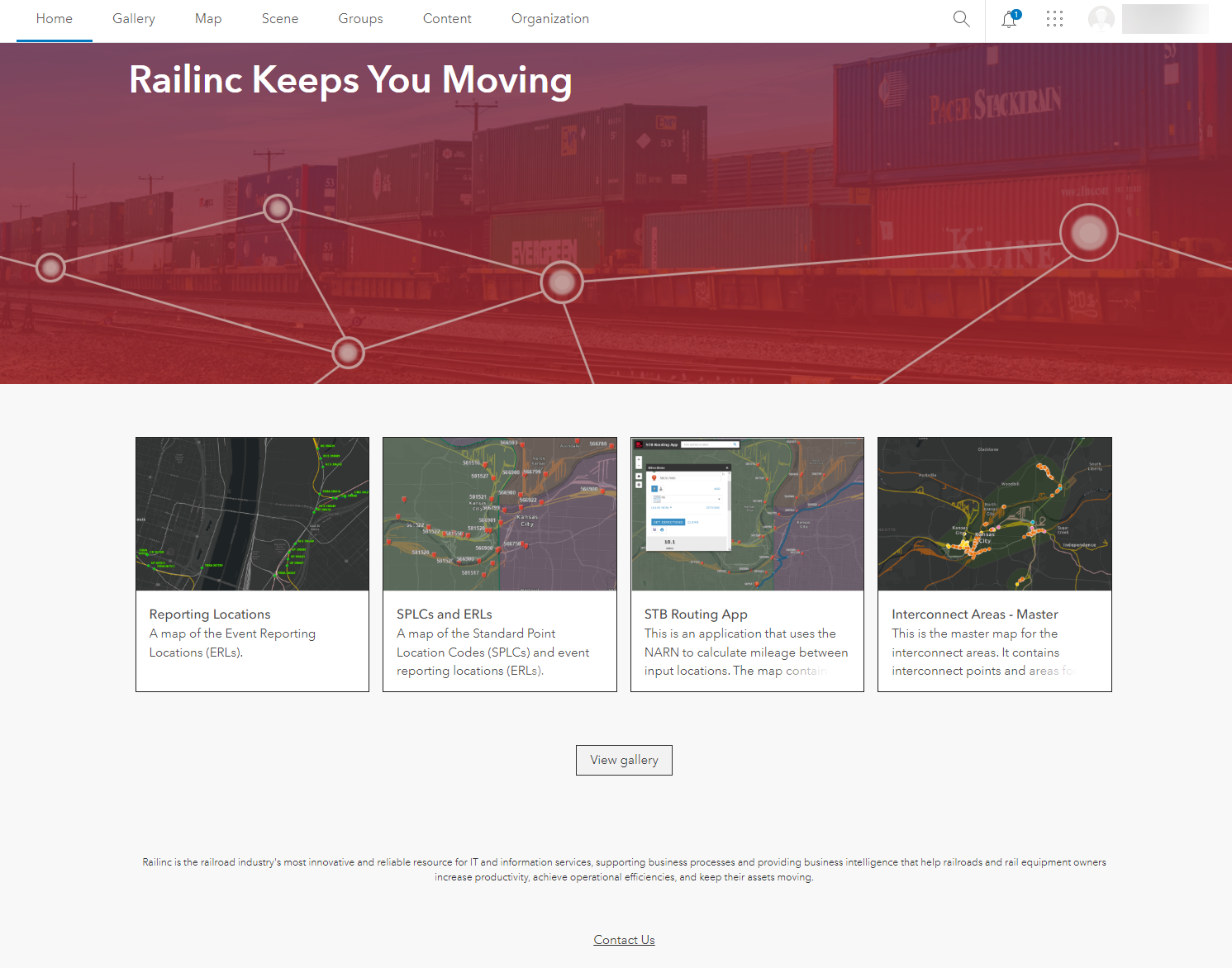
RIGIS Data Exchange
The RIGIS Data Exchange application enables the railroad industry to upload GIS data associated with their assets using business rules established by the AAR GIS Committee in the industry standard RIGIS data exchange schema.
RIGIS Data Exchange Application
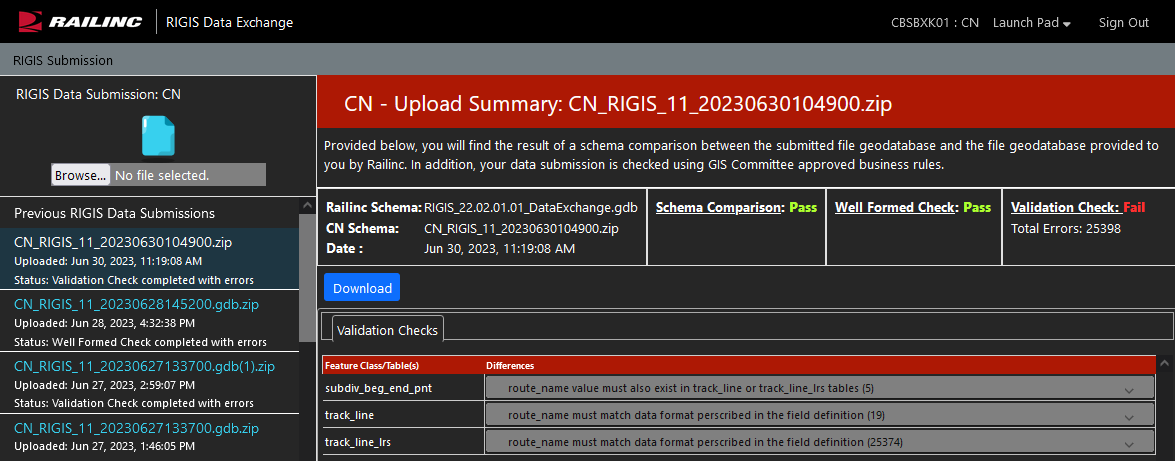
ERL Dashboard
The Event Reporting Location (ERL) Dashboard application enables users to review and compare the geographic location of one ERL to another ERL.
The first version of the application specifically includes an analysis of data in the Centralized Station Master (CSM) compared to data provided by the railroad’s GIS team. Through the ERL Dashboard application, the Railinc Location Management team provides a simple way for end users to search for CSM locations based on Standard Carrier Alpha Code (SCAC), Standard Point Location Code (SPLC), Freight Station Accounting Code (FSAC), or Station Name. After locating a station, a user can see the difference between the data in the CSM and the data that the GIS team from their railroad has provided. If there is a difference between the data, the geographic information is highlighted in red in the ERL Dashboard.
ERL Dashboard Showing Data Discrepancies
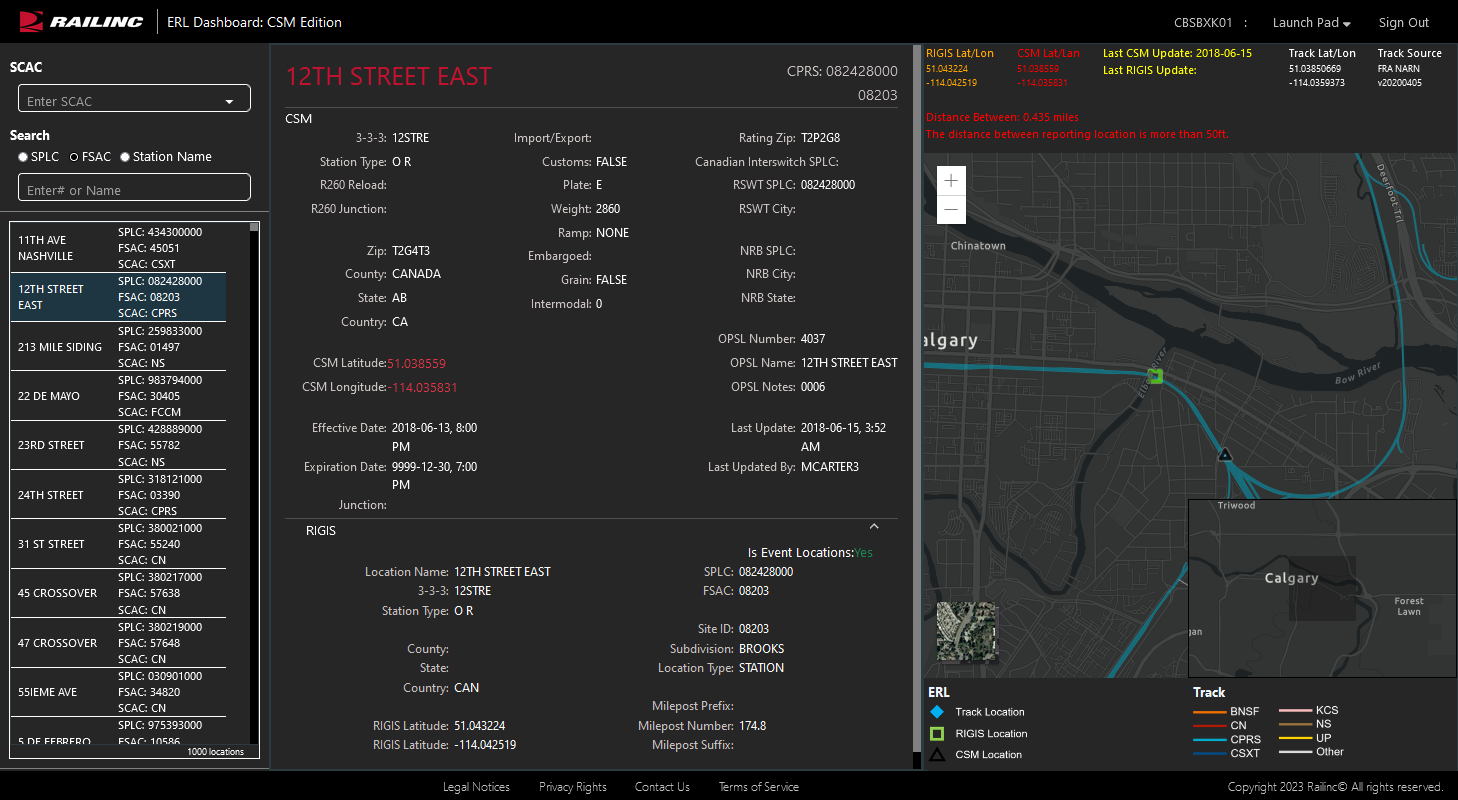
In the image above, the map shows the location provided by the railroad's GIS team and the location contained in the CSM. The geographic location (latitude and longitude) are shown in red text because the two locations are greater than 50 feet from each other.
Once users identify GIS data discrepancies using the ERL Dashboard, they can then make the appropriate updates in the CSM, which is considered the system of record.
